

According to the “State of Cloud Security: Are Businesses Addressing Key Vulnerabilities in 2024?” survey conducted by CDNetworks, 20% of respondents admitted experiencing a major cyber attack at least once in the last 12 months. Meanwhile, 40% said they were unsure.
Although the percentages of companies directly impacted may seem relatively low at first glance, it’s concerning that 1 in 5 organisations have been affected (some more than once). Additionally, the number of ‘unsure’ responses points to a potential preparedness gap. Many organisations may be unknowingly exposed due to a lack of awareness or insufficient resources dedicated to cybersecurity.

AOPG Insights recently partnered with CDNetworks, a global leader in Content Delivery Networks (CDN), and conducted a micro-survey—titled “State of Cloud Security: Are Businesses Addressing Key Vulnerabilities in 2024?”—to assess cloud security readiness among organisations in the region. The findings were mixed, offering encouraging insights that suggest progress, but also highlighting areas of concern that require immediate attention.
Key takeaways include:
• Cybersecurity Gaps: Companies see the need for cybersecurity but lack readiness and resources in API security, monitoring, and threat intelligence.
• Mixed Practices: While awareness and multi-layered cloud security are improving, gaps in API management and data security persist.
• MSSP Interest: Growing interest in Managed Security Service Providers (MSSPs) reflects a need for enhanced security and support for resource-limited companies.
Find out more about the survey, its findings, and recommendations HERE.
Click here to download the survey now
While the cloud offers immense benefits for businesses, it also presents a new attack surface for malicious actors, whose means of attack have only grown more sophisticated. Some of the most serious threats to the cloud are as follows:
• Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) Attacks: These attacks overwhelm a system with traffic, making it unavailable to legitimate users’ environments.
• Automated Bot Attacks: Malicious bots can be used to automate tasks such as credential stuffing, account takeover attempts, and scraping sensitive data.
• Ransomware: This type of malware encrypts an organisation’s data, rendering it inaccessible until a ransom is paid.
• SQL Injection: Attackers exploit vulnerabilities in web applications to inject malicious code that can steal sensitive data.
• Cross-Site Scripting (XSS): Hackers inject malicious scripts into websites that can steal user data or redirect them to phishing sites.
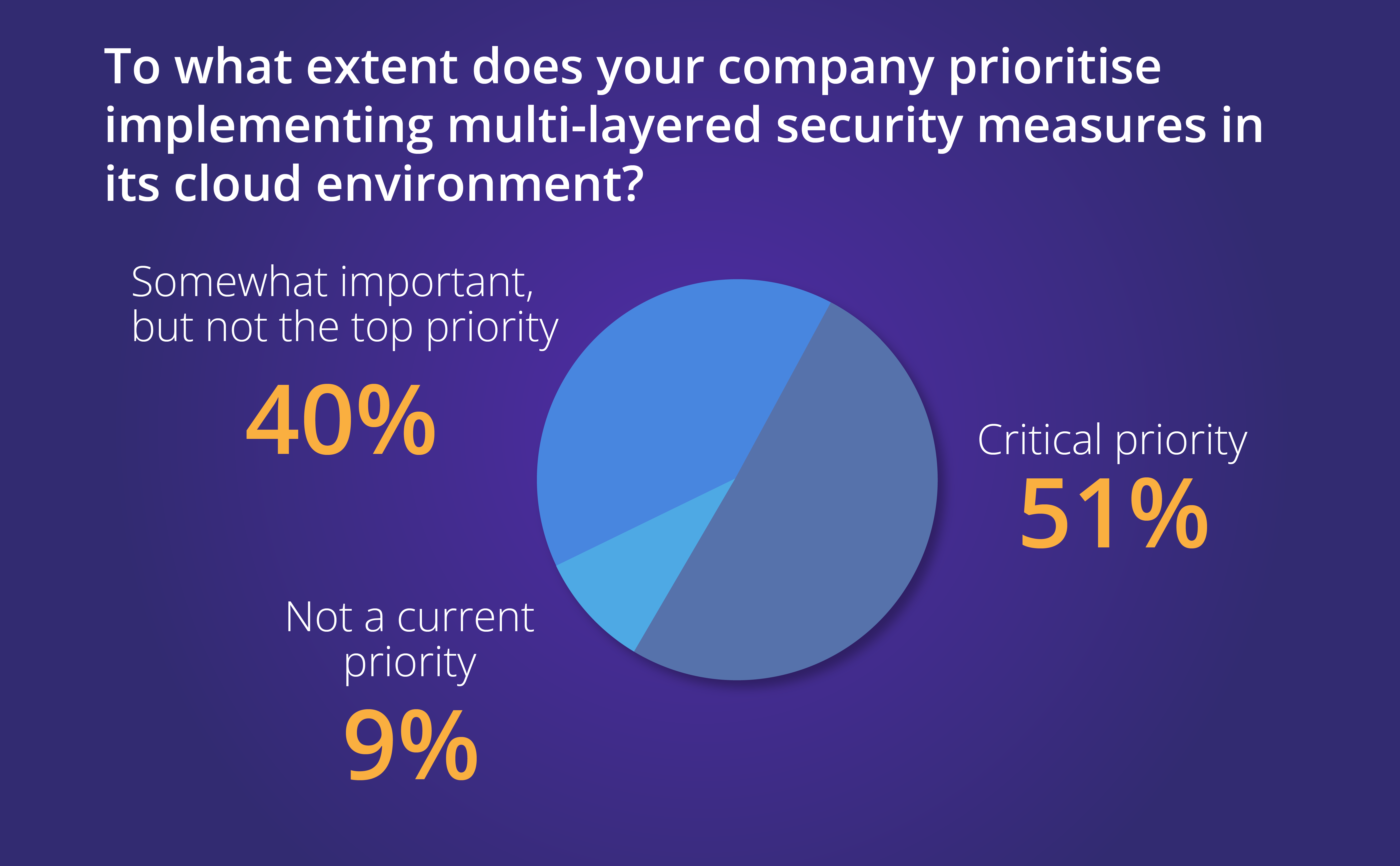
In its “State of Cloud Security: Are Businesses Addressing Key Vulnerabilities in 2024?” report, CDNetworks recommends that organisations implement a defence-in-depth security strategy.
In this multi-layered approach, various security controls are implemented to safeguard the organisation’s cloud environments from a range of threats. If one layer is breached, the subsequent layers are designed to contain and mitigate the threat, effectively preventing it from compromising the organisation’s network and cloud infrastructure.
It is an encompassing strategy for cloud security, and the results of the CDNetworks survey indicate a growing recognition of the importance of cloud security, as over half (51%) of the respondents have prioritised implementing multi-layered security measures.